Hospitals are centers of healing, but they can also be hotspots for infections if proper hygiene and sanitation are not maintained. Ensuring cleanliness is not just about appearances; it is a critical aspect of patient safety, staff well-being, and infection prevention. In today’s healthcare environment, hygiene and sanitation play a pivotal role in maintaining high standards of care and preventing hospital-acquired infections (HAIs).
This comprehensive guide explores the importance of hygiene and sanitation in hospitals, best practices, challenges, and strategies for maintaining a safe and healthy environment.
Why Hygiene and Sanitation Are Critical in Hospitals
Maintaining hygiene and sanitation in hospitals is crucial for several reasons:
1. Prevention of Hospital-Acquired Infections (HAIs)
Hospital-acquired infections, also known as nosocomial infections, can occur due to bacteria, viruses, or fungi present in the hospital environment.
Impact of HAIs:
- Prolonged hospital stays.
- Increased medical costs.
- Higher morbidity and mortality rates.
- Damage to the hospital’s reputation.
Proper sanitation reduces the risk of HAIs, protecting both patients and healthcare workers.
2. Protecting Healthcare Workers
Healthcare workers are on the frontlines of patient care and are at high risk of exposure to infectious agents.
Benefits of hygiene:
- Reduces the risk of occupational infections.
- Promotes a safe working environment.
- Encourages adherence to infection control protocols.
3. Enhancing Patient Trust and Satisfaction
Patients are more likely to trust and feel comfortable in a clean, well-maintained hospital environment.
Advantages:
- Improves patient confidence in the care provided.
- Supports faster recovery by reducing infection risks.
- Enhances overall patient experience and satisfaction.
Key Areas of Hospital Hygiene
Hospital hygiene encompasses multiple areas, each critical for preventing infections.
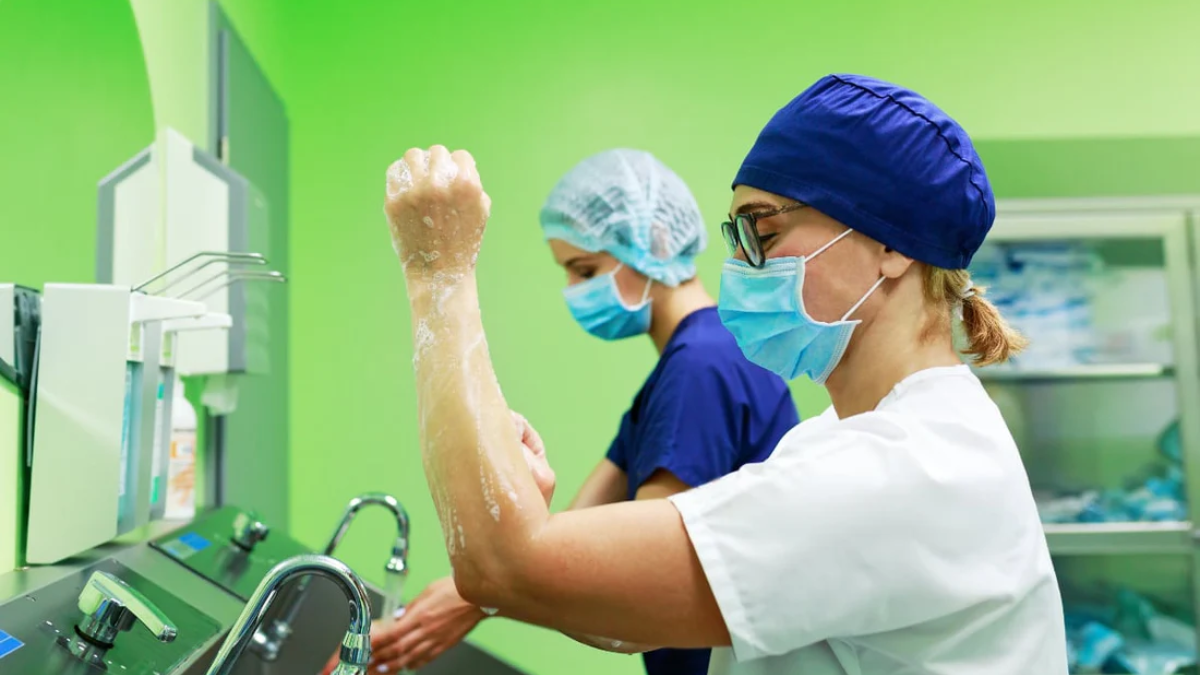
1. Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene is the most effective measure to prevent the spread of infections.
Best Practices:
- Regular handwashing with soap and water.
- Using alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
- Proper hand hygiene before and after patient contact.
- Educating staff, patients, and visitors about hand hygiene.
2. Cleaning of Surfaces and Equipment
Surfaces and medical equipment can harbor pathogens if not cleaned regularly.
Guidelines:
- Regular disinfection of high-touch surfaces like bed rails, doorknobs, and medical devices.
- Using approved disinfectants for various surfaces.
- Sterilization of surgical instruments and diagnostic tools.
- Scheduled deep cleaning of patient rooms, ICUs, and operation theaters.
3. Waste Management
Hospitals generate hazardous and non-hazardous waste. Proper segregation and disposal are crucial.
Practices include:
- Segregating waste into biohazard, sharps, recyclable, and general waste.
- Safe disposal of needles, syringes, and medical waste.
- Using color-coded bins and following national regulations.
- Regular staff training on waste handling procedures.
4. Water and Sanitation Facilities
Clean water and sanitation facilities are vital for infection control.
Measures:
- Regular monitoring of water quality.
- Proper maintenance of toilets, bathrooms, and sinks.
- Availability of handwashing stations and sanitizers.
- Proper drainage and sewage management.
Hygiene Protocols in Different Hospital Departments
Each department has unique requirements for maintaining hygiene.
1. Emergency Department (ER)
- Rapid cleaning of beds, stretchers, and equipment after each patient.
- Immediate disposal of contaminated materials.
- Hand hygiene enforcement for all staff.
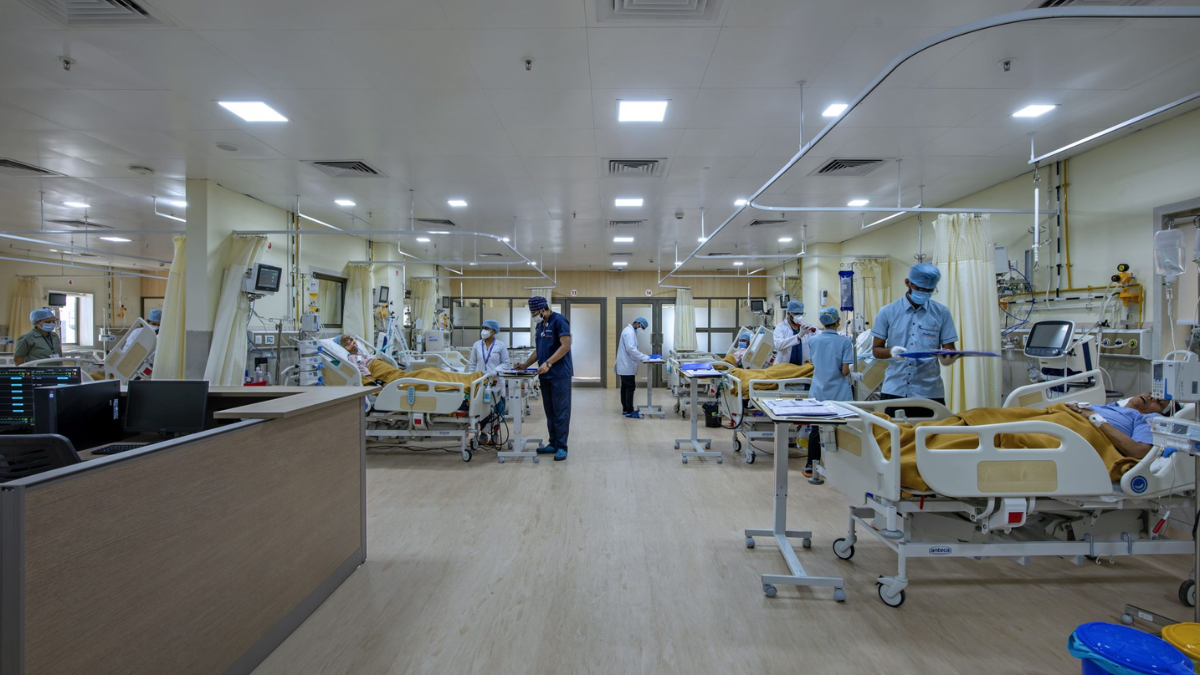
2. Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
- Frequent disinfection of monitors, ventilators, and medical instruments.
- Sterile procedures for invasive devices like catheters and IV lines.
- Strict hand hygiene compliance for all healthcare workers.
3. Operation Theaters (OT)
- Strict sterilization protocols for surgical instruments.
- Controlled air quality with HEPA filters.
- Use of disposable gowns, gloves, and drapes.
4. Outpatient Departments (OPD)
- Regular cleaning of waiting areas, chairs, and counters.
- Hand sanitizers for patients and staff.
- Monitoring for overcrowding to maintain hygiene.
Role of Hospital Staff in Hygiene Maintenance
Hospital staff are the frontline defenders of hygiene and sanitation.
Responsibilities of Healthcare Workers
- Adhering to hand hygiene protocols.
- Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Proper handling and disposal of medical waste.
- Reporting and addressing hygiene issues promptly.
Training and Awareness
- Regular workshops and refresher courses on infection control.
- Awareness campaigns about HAIs and preventive measures.
- Encouraging a culture of safety and cleanliness.
Innovative Hygiene Practices in Modern Hospitals
Modern hospitals are adopting advanced methods to enhance hygiene and sanitation.
1. Use of UV-C Light and Robotics
- UV-C light for disinfecting rooms and equipment.
- Robots for automated cleaning and sanitization of high-traffic areas.
2. Antimicrobial Surfaces
- Using copper or antimicrobial coatings on high-touch surfaces.
- Reduces bacterial growth and cross-contamination.
3. Smart Hand Hygiene Systems
- Sensors to monitor hand hygiene compliance among staff.
- Automated reminders to encourage regular handwashing.
4. Air Purification Systems
- HEPA filters and negative pressure rooms to prevent airborne infections.
- Reduces the risk of respiratory pathogen transmission.
Challenges in Maintaining Hospital Hygiene
Despite best efforts, hospitals face challenges in maintaining high hygiene standards.
Common Challenges
- High patient load and overcrowding.
- Limited resources for cleaning and waste management.
- Staff non-compliance with hygiene protocols.
- Complex hospital layouts making thorough cleaning difficult.
- Emerging drug-resistant infections requiring advanced disinfection methods.
Addressing these challenges requires continuous monitoring, training, and investment in hygiene infrastructure.
Government Regulations and Accreditation Standards
Hospital hygiene is regulated by national and international standards to ensure patient safety.
Key Regulations
- Guidelines by the World Health Organization (WHO) for infection prevention.
- National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) standards.
- Local health department regulations for sanitation, waste management, and infection control.
Compliance with these standards ensures hospitals maintain high levels of hygiene and patient care.
Patient Role in Hospital Hygiene
Patients and visitors also play a role in maintaining hospital hygiene.
Tips for Patients and Visitors
- Follow hand hygiene guidelines and use sanitizers.
- Adhere to visitor restrictions in sensitive areas like ICUs.
- Avoid bringing unnecessary items that can carry germs.
- Report spills, unclean areas, or potential hazards to hospital staff.
Patient participation complements staff efforts in creating a safe environment.
Conclusion
Hygiene and sanitation are the foundation of safe and effective healthcare. Maintaining high standards of cleanliness in hospitals prevents infections, protects patients and staff, and enhances overall patient satisfaction.
By implementing strict protocols, investing in modern cleaning technologies, training staff, and involving patients, hospitals can provide safe, high-quality care while reducing the risk of hospital-acquired infections.
Green and eco-friendly practices, combined with traditional hygiene methods, ensure hospitals not only heal patients but also maintain a healthy and sustainable environment.